What’s Happening to Jupiter’s Great Red Spot? The Solar System’s Largest Storm Could Finally Disappear
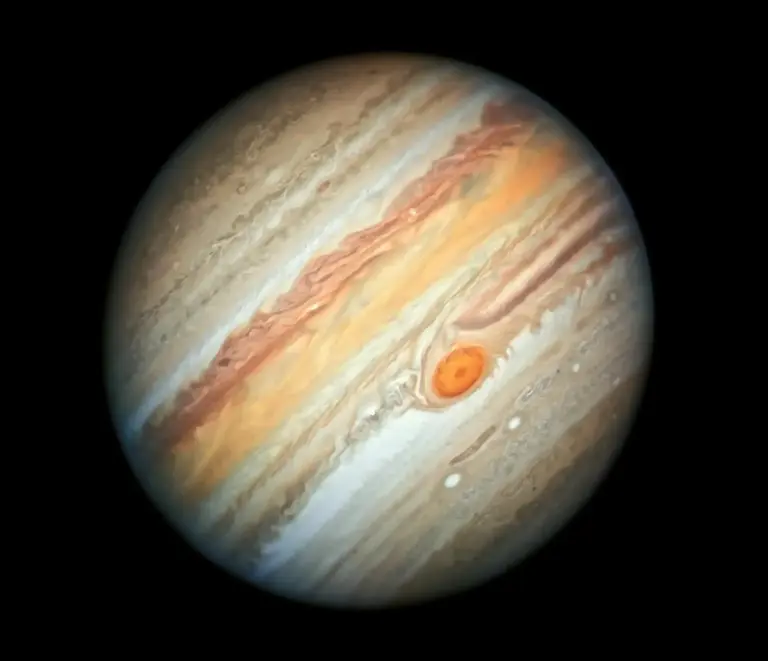 Jupiter’s Great Red Spot (GRS), an easily visible anticyclonic vortex and the largest such vortex in the Solar System, has intrigued scientists since it was first observed through telescopes centuries ago. Recent research, including simulations and space mission data, has investigated its formation, stability, and the possibility of it shrinking or disappearing in the future. Credit: NASA, ESA, A. Simon (Goddard Space Flight Center), and M.H. Wong (University of California, Berkeley)
Jupiter’s Great Red Spot (GRS), an easily visible anticyclonic vortex and the largest such vortex in the Solar System, has intrigued scientists since it was first observed through telescopes centuries ago. Recent research, including simulations and space mission data, has investigated its formation, stability, and the possibility of it shrinking or disappearing in the future. Credit: NASA, ESA, A. Simon (Goddard Space Flight Center), and M.H. Wong (University of California, Berkeley)
Jupiter’s Great Red Spot is a giant vortex that has existed for at least 190 years. Recent studies suggest it is distinct from an earlier observed spot, and simulations explore how Jupiter’s winds may have shaped it. The GRS has been shrinking, and future research will focus on its sustainability and potential future disintegration.
Jupiter’s Great Red Spot (GRS) stands out as one of the most iconic features in the Solar System. This massive atmospheric structure, currently spanning a diameter equal to that of Earth, is easily recognizable due to its striking reddish hue, which contrasts sharply with Jupiter’s pale cloud tops. Even small telescopes can capture its distinct appearance. The GRS is a gigantic anticyclonic vortex, with winds reaching speeds of 450 km/h along its outer edges. It holds the title of the largest and longest-lasting vortex in the atmospheres of any planet in our Solar System. However, the exact age of the GRS is still debated, and the processes behind its formation remain a mystery.
Speculation about the origin of the GRS dates back to the first telescopic observations made by the astronomer Giovanni Domenico Cassini, who in 1665 discovered a dark oval at the same latitude as the GRS and named it the ‘Permanent Spot’ (PS), since it was observed by him and other astronomers until 1713.
Track of it was subsequently lost for 118 years and it was not until 1831 and later years that S. Schwabe again observed a clear structure, roughly oval in shape and at the same latitude as the GRS; that can be regarded as the first observation of the current GRS, perhaps of a nascent GRS. Since then, the GRS has been observed regularly by means of telescopes and by the various space missions that have visited the planet right up to the present day.
Analyzing the GRS’s Evolution
In the study, the authors first analyzed the evolution of its size over time, its structure, and the movements of both meteorological formations, the former PS and the GRS; to do so, they used historical sources dating back to the mid-17th century, shortly after the invention of the telescope.
 From left to right: Enrique García-Melendo (UPC) Agustín Sánchez Lavega and Jon Legarreta (UPV/EHU). Credit: Fernando Gómez. UPV/EHU
From left to right: Enrique García-Melendo (UPC) Agustín Sánchez Lavega and Jon Legarreta (UPV/EHU). Credit: Fernando Gómez. UPV/EHU
“From the measurements of sizes and movements, we deduced that it is highly unlikely that the current GRS was the PS observed by G. D. Cassini. The PS probably disappeared sometime between the mid-18th and 19th centuries, in which case we can say that the longevity of the Red Spot now exceeds 190 years at least,” explained Agustín Sánchez-Lavega, professor of physics at the UPV/EHU and who led this research. The Red Spot, which in 1879 was 39,000 km in size at its longest axis, has been shrinking to about the current 14,000 km and simultaneously becoming more rounded.
Recent Findings and Simulation Studies
What is more, since the 1970s several space missions have studied this meteorological phenomenon closely. Recently, “various instruments on board the Juno mission in orbit around Jupiter have shown that the GRS is shallow and thin when compared to its horizontal dimension, as vertically it is about 500 km long,” explained Sánchez-Lavega.
To find out how this immense vortex could have formed, the UPV/EHU and UPC teams carried out numerical simulations on Spanish supercomputers, such as the BSC’s MareNostrum IV, part of the Spanish Supercomputing Network (RES), using two types of complementary models of the behavior of thin vortices in Jupiter’s atmosphere. Predominating on the giant planet are intense wind currents that flow along the parallels alternating in their direction with the latitude. To the north of the GRS, winds blow in a westerly direction at speeds of 180 km/h while to the south, they blow in the opposite direction, in an easterly direction, at speeds of 150 km/h. This generates a huge north-south shear in wind speed, which is a basic ingredient enabling the vortex to grow inside it.
In the research, a range of mechanisms were explored to explain the genesis of the GRS, including the eruption of a gigantic superstorm, similar to those rarely observed on the twin planet Saturn, or the merging of multiple smaller vortices produced by wind shear. The results indicate that, although an anticyclone forms in both cases, it differs in terms of shape and dynamic properties from those of the present GRS. “We also think that if one of these unusual phenomena had occurred, it or its consequences in the atmosphere must have been observed and reported by the astronomers at the time,” said Sánchez-Lavega.
Numerical Simulations and Future Research
In a third set of numerical experiments, the research team explored the generation of the GRS from a known instability in the winds that is thought to be capable of producing an elongated cell that encloses and traps them. Such a cell would be a proto-GRS, a nascent Red Spot, whose subsequent shrinkage would give rise to the compact and rapidly rotating GRS observed in the late 19th century. The formation of large elongated cells has already been observed in the genesis of other major vortices on Jupiter.
“In our simulations, supercomputers enabled us to discover that the elongated cells are stable when they rotate around the periphery of the GRS at the speed of Jupiter’s winds, as would be expected when they form because of this instability,” said Enrique García-Melendo, researcher in the UPC’s Department of Physics. Using two different types of numerical models, one at the UPV/EHU and the other at the UPC, the researchers concluded that if the rotational speed of the proto-GRS is lower than that of the surrounding winds, the proto-GRS will break up, making the formation of a stable vortex impossible. And, if it is very high, the properties of the proto-GRS differ from those of the current GRS.
Future research will aim to try and reproduce the shrinkage of the GRS over time in order to find out, in greater detail, the physical mechanisms underlying its sustainability over time. At the same time, it will try to predict whether the GRS will disintegrate and disappear when it reaches a size limit, as might have occurred to Cassini’s PS, or whether it will stabilize at a size limit at which it may last for many more years.
Reference: “The Origin of Jupiter’s Great Red Spot” by Agustín Sánchez-Lavega, Enrique García-Melendo, Jon Legarreta, Arnau Miró, Manel Soria and Kevin Ahrens-Velásquez, 16 June 2024, Geophysical Research Letters. DOI: 10.1029/2024GL108993
0 人喜欢
There is no comment, let's add the first one.